A1: Control of Citrobacter rodentium by oxygen-dependent B cell regulation
A1: Control of Citrobacter rodentium by oxygen-dependent B cell regulation
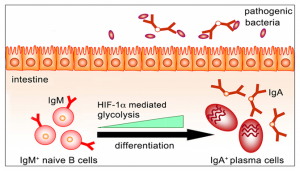
Citrobacter rodentium is a murine model pathogen for human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, which colonizes the lumen and mucosal surface of the colon. It was previously shown that defenses against C. rodentium depends on B cells, IgA antibodies and Th17 activation. Recently, we have shown that HIF-1α induces regulatory B cell expansion and IL-10 production. It is likely that IL-10 produced by regulatory B cells protects against gut epithelial cell damage by suppression of Th1 and Th17 cell functions. Our preliminary data suggest that IgA positive plasma cells are also dependent of HIF-1α expression. In this project, we will characterize antibody production in the intestine of HIF-1α deficient in B cells in the context of dysbioses. Furthermore, we will determine the impact of HIF-1α deficiency in B cells during C. rodentium oral infection. RNA sequencing methodology and multi-color flow cytometry will be used to characterize IgA plasma cell in steady state and during C. rodentium infection.
Supervisor
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Aline Bozec
91054 Erlangen
- Phone number: +49 9131 85-29314
- Email: bozec.aline@outlook.com
- Website: https://www.medizin3.uk-erlangen.de/forschung/arbeitsgruppen/ag-prof-dr-a-bozec/